Giới thiệu
Bài viết với chủ đề Higher Order Functions dành cho những người mới tiếp cận với Kotlin.
Nếu như các bạn là một lập trình viên Android đi lên từ Java, chắc chắn sẽ nhận xét rằng Kotlin thật sự rất "kool ngầu". Một trong những thứ tạo nên điều diệu kỳ này chính là việc hỗ trợ lập trình hàm. Tức là các hàm (functions) có thể được truyền vào như một biến của hàm khác, và cũng có thể được trả về từ một hàm nào đó. Đấy chính là Higher Order Function.
Định nghĩa về một Higher Order Function
Chúng ta cùng xem một ví dụ cơ bản sau đây
//A simple Higher Order Function in Kotlin
//This function accepts three parameters
//And the last parameter is a function
fun rollDice(
range: IntRange,
time: Int,
callback: (result: Int) -> Unit
) {
for (i in 0 until time) {
val result = range.random()
//As the last parameter is a function
//we can call it as a function
callback(result)
}
}
Trong 3 tham số truyền vào của hàm rollDice, thì tham số thứ ba chính là một function
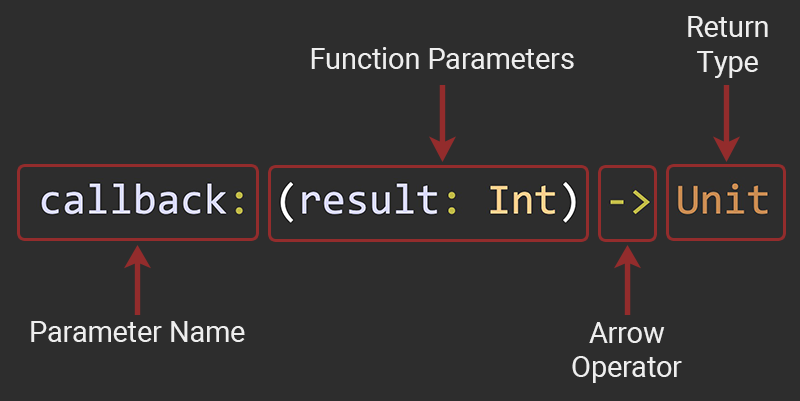 Trong đó,
Trong đó, callback chính là tên của functions, đồng thời là tên của tham số truyền vào. (result: Int) lại chính là tham số của callback.
Còn Unit chính là kiểu trả về của function. Trong trường hợp này, nó không cần trả về gì cả.
Tiếp theo chúng ta gọi Higher Order Function.
fun main() {
rollDice(1..6, 3, { result ->
println(result)
})
}
Ở đây, result chính là tham số của hàm callback. Lệnh println chính là công việc thực hiện tương ứng với hàm callback ở trên.
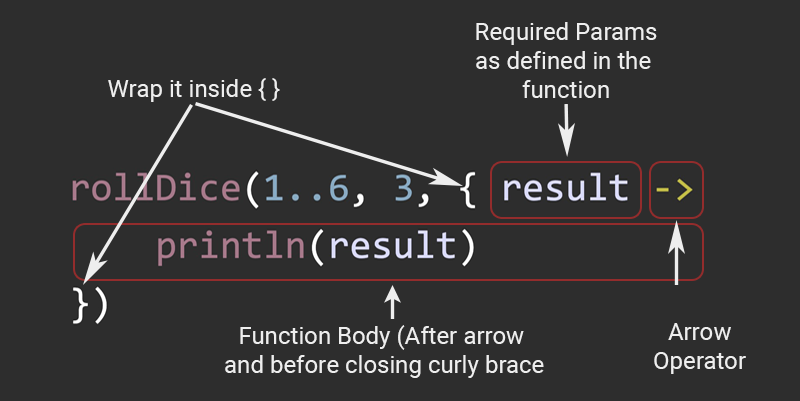
Xem ví dụ thực tiễn
Sau đây chúng ta đến với một vài đường code nhé.
class ExampleDialog(
context: Context,
private val onProcessClick: (dialog: Dialog) -> Unit
) : BaseDialog(context = context) {
override val isCancelable: Boolean
get() = true
override fun initView() {
this.setContentView(R.layout.example_dialog)
val button = this.findViewById<Button>(R.id.process_btn)
button.setSingleClick {
dismiss()
onProcessClick(this)
}
}
}
Tại nơi muốn show Dialog.
ExampleDialog(requireContext()) {
doAnyThing()
//this func will implement when onProcessClick(this) is called
}.show()
Thêm một ví dụ khác nhé, cũng là ExampleDialog trên nhưng với 2 callbacks.
class ExampleDialog(
context: Context,
private val onPreventClick: (dialog: Dialog) -> Unit
private val onProcessClick: (dialog: Dialog) -> Unit
) : BaseDialog(context = context) {
override val isCancelable: Boolean
get() = true
override fun initView() {
this.setContentView(R.layout.example_dialog)
val button = this.findViewById<Button>(R.id.process_btn)
button.setSingleClick {
dismiss()
onProcessClick(this)
}
val button01 = this.findViewById<Button>(R.id.prevent_btn)
button01.setSingleClick {
dismiss()
onPreventClick(this)
}
}
}
Và đây là bên hàm gọi Dialog:
ExampleDialog(requireContext(), {
doPreventClickHandle()
}, {
doProcessClickHandle()
}).show()
Hy vọng những ví dụ trên sẽ cho bạn những cái nhìn thực tế hơn về Higher Order Function. Chúng không những hữu dụng mà còn rất kool ngầu phải không nào !!!